Triangular Prism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
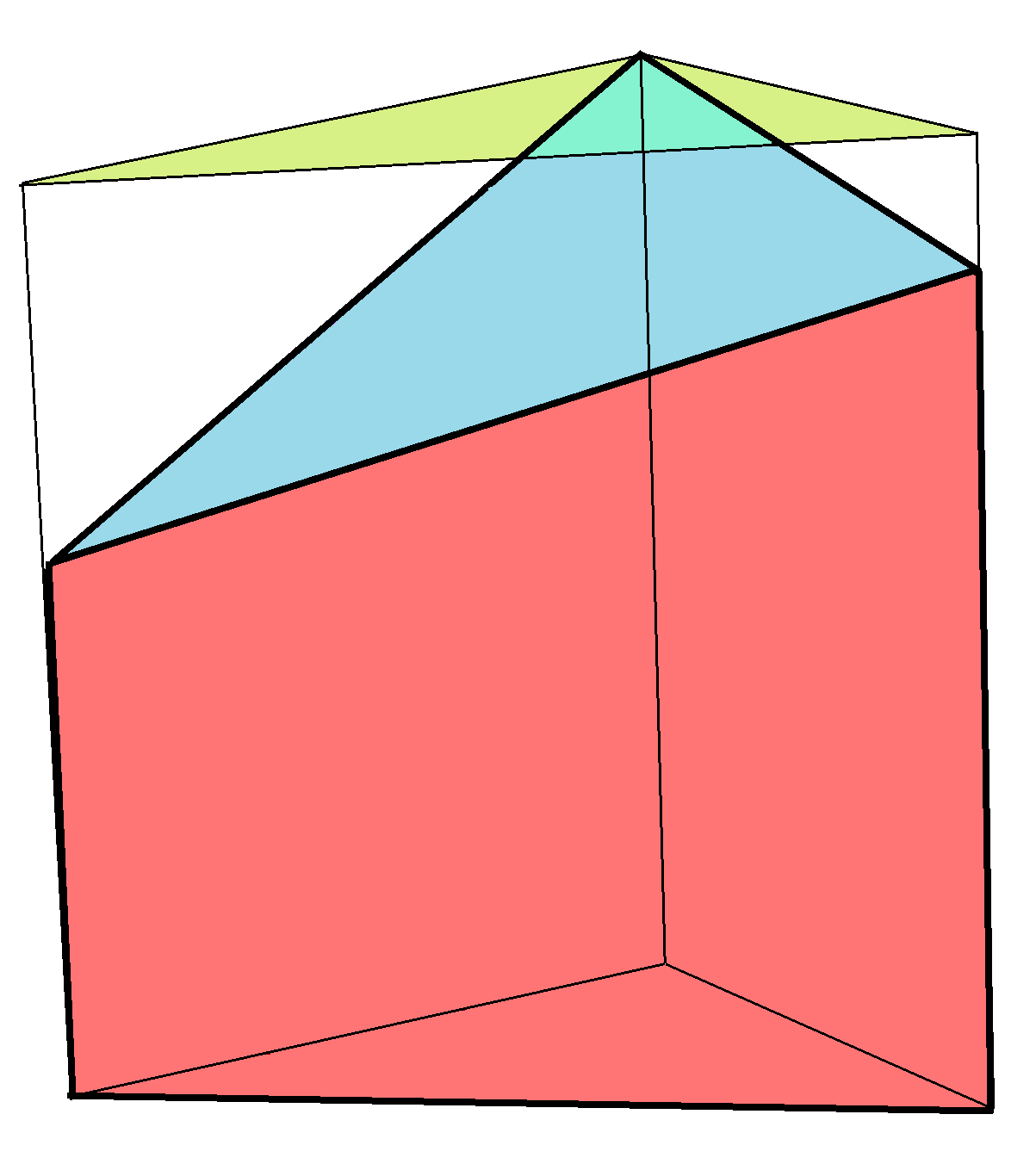 The volume of a truncated triangular prism with base area ''A'' and the three heights ''h''1, ''h''2, and ''h''3 is determined by
::
The volume of a truncated triangular prism with base area ''A'' and the three heights ''h''1, ''h''2, and ''h''3 is determined by
::

Interactive Polyhedron: Triangular Prism
Surface area and volume of a triangular prism
Prismatoid polyhedra Space-filling polyhedra
geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is c ...
, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism
Prism usually refers to:
* Prism (optics), a transparent optical component with flat surfaces that refract light
* Prism (geometry), a kind of polyhedron
Prism may also refer to:
Science and mathematics
* Prism (geology), a type of sedimentary ...
; it is a polyhedron
In geometry, a polyhedron (plural polyhedra or polyhedrons; ) is a three-dimensional shape with flat polygonal faces, straight edges and sharp corners or vertices.
A convex polyhedron is the convex hull of finitely many points, not all on th ...
made of a triangular
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices ''A'', ''B'', and ''C'' is denoted \triangle ABC.
In Euclidean geometry, any three points, when non- collinea ...
base, a translated
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides
In geometry, the tests for congruence and similarity involve comparing corresponding sides and corresponding angles of polygons. In these tests, each side and each angle in one polygon is paired with a side or angle in the second polygon, ta ...
. A right triangular prism has rectangular
In Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is a quadrilateral with four right angles. It can also be defined as: an equiangular quadrilateral, since equiangular means that all of its angles are equal (360°/4 = 90°); or a parallelogram containin ...
sides, otherwise it is ''oblique''. A uniform triangular prism is a right triangular prism with equilateral bases, and square sides.
Equivalently, it is a polyhedron of which two faces are parallel, while the surface normal
In geometry, a normal is an object such as a line, ray, or vector that is perpendicular to a given object. For example, the normal line to a plane curve at a given point is the (infinite) line perpendicular to the tangent line to the curve at ...
s of the other three are in the same plane (which is not necessarily parallel to the base planes). These three faces are parallelogram
In Euclidean geometry, a parallelogram is a simple (non- self-intersecting) quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. The opposite or facing sides of a parallelogram are of equal length and the opposite angles of a parallelogram are of equa ...
s. All cross-sections parallel to the base faces are the same triangle.
As a semiregular (or uniform) polyhedron
A right triangular prism is semiregular or, more generally, auniform polyhedron
In geometry, a uniform polyhedron has regular polygons as faces and is vertex-transitive (i.e., there is an isometry mapping any vertex onto any other). It follows that all vertices are congruent.
Uniform polyhedra may be regular (if also fa ...
if the base faces are equilateral triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three Edge (geometry), edges and three Vertex (geometry), vertices. It is one of the basic shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices ''A'', ''B'', and ''C'' is denoted \triangle ABC.
In Euclidean geometry, an ...
s, and the other three faces are squares
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90- degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length a ...
. It can be seen as a truncated trigonal hosohedron
In spherical geometry, an -gonal hosohedron is a tessellation of lunes on a spherical surface, such that each lune shares the same two polar opposite vertices.
A regular -gonal hosohedron has Schläfli symbol with each spherical lune ha ...
, represented by Schläfli symbol
In geometry, the Schläfli symbol is a notation of the form \ that defines regular polytopes and tessellations.
The Schläfli symbol is named after the 19th-century Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli, who generalized Euclidean geometry to more ...
t. Alternately it can be seen as the Cartesian product
In mathematics, specifically set theory, the Cartesian product of two sets ''A'' and ''B'', denoted ''A''×''B'', is the set of all ordered pairs where ''a'' is in ''A'' and ''b'' is in ''B''. In terms of set-builder notation, that is
: A\ti ...
of a triangle and a line segment
In geometry, a line segment is a part of a straight line that is bounded by two distinct end points, and contains every point on the line that is between its endpoints. The length of a line segment is given by the Euclidean distance between ...
, and represented by the product, The dual of a triangular prism is a triangular bipyramid
In geometry, the triangular bipyramid (or dipyramid) is a type of hexahedron, being the first in the infinite set of face-transitive bipyramids. It is the dual of the triangular prism with 6 isosceles triangle faces.
As the name suggests, i ...
.
The symmetry group
In group theory, the symmetry group of a geometric object is the group of all transformations under which the object is invariant, endowed with the group operation of composition. Such a transformation is an invertible mapping of the ambient ...
of a right 3-sided prism with triangular base is ''D3h'' of order 12. The rotation group
In mathematics, the orthogonal group in dimension , denoted , is the group of distance-preserving transformations of a Euclidean space of dimension that preserve a fixed point, where the group operation is given by composing transformations. ...
is ''D3'' of order 6. The symmetry group does not contain inversion
Inversion or inversions may refer to:
Arts
* , a French gay magazine (1924/1925)
* ''Inversion'' (artwork), a 2005 temporary sculpture in Houston, Texas
* Inversion (music), a term with various meanings in music theory and musical set theory
* ...
.
Volume
The volume of any prism is the product of the area of the base and the distance between the two bases. In this case the base is a triangle so we simply need to compute the area of the triangle and multiply this by the length of the prism: : where is the length of one side of the triangle, is the length of analtitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context ...
drawn to that side, and is the distance between the triangular faces.
Truncated triangular prism
A ''truncated right triangular prism'' has one triangular face truncated ( planed) at an oblique angle. : The volume of a truncated triangular prism with base area ''A'' and the three heights ''h''1, ''h''2, and ''h''3 is determined by
::
The volume of a truncated triangular prism with base area ''A'' and the three heights ''h''1, ''h''2, and ''h''3 is determined by
::
Facetings
There are two full D3h symmetryfaceting
Stella octangula as a faceting of the cube
In geometry, faceting (also spelled facetting) is the process of removing parts of a polygon, polyhedron or polytope, without creating any new vertices.
New edges of a faceted polyhedron may be cre ...
s of a ''triangular prism'', both with 6 isosceles triangle
In geometry, an isosceles triangle () is a triangle that has two sides of equal length. Sometimes it is specified as having ''exactly'' two sides of equal length, and sometimes as having ''at least'' two sides of equal length, the latter versio ...
faces, one keeping the original top and bottom triangles, and one the original squares. Two lower C3v symmetry facetings have one base triangle, 3 lateral crossed square faces, and 3 isosceles triangle lateral faces.
Related polyhedra and tilings

Symmetry mutations
This polyhedron is topologically related as a part of sequence of uniform truncated polyhedra withvertex configuration
In geometry, a vertex configurationCrystallography ...
s (3.2n.2n), and ,3Coxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H. S. M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of reflections (or kaleidoscopic mirrors). Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean refl ...
symmetry.
This polyhedron is topologically related as a part of sequence of cantellated polyhedra with vertex figure (3.4.n.4), and continues as tilings of the hyperbolic plane
In mathematics, hyperbolic geometry (also called Lobachevskian geometry or Bolyai– Lobachevskian geometry) is a non-Euclidean geometry. The parallel postulate of Euclidean geometry is replaced with:
:For any given line ''R'' and point ''P' ...
. These vertex-transitive
In geometry, a polytope (e.g. a polygon or polyhedron) or a tiling is isogonal or vertex-transitive if all its vertices are equivalent under the symmetries of the figure. This implies that each vertex is surrounded by the same kinds of face in ...
figures have (*n32) reflectional symmetry
Symmetry (from grc, συμμετρία "agreement in dimensions, due proportion, arrangement") in everyday language refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, "symmetry" has a more precise definit ...
.
Compounds
There are 4 uniform compounds of triangular prisms: :Compound of four triangular prisms
This uniform polyhedron compound is a Chirality (mathematics), chiral symmetric arrangement of 4 triangular prisms, aligned with the axes of three-fold rotational symmetry of an octahedron.
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the ve ...
, compound of eight triangular prisms
This uniform polyhedron compound is a symmetric arrangement of 8 triangular prisms, aligned in pairs with the axes of three-fold rotational symmetry of an octahedron
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron ...
, compound of ten triangular prisms
This uniform polyhedron compound is a Chirality (mathematics), chiral symmetric arrangement of 10 triangular prisms, aligned with the axes of three-fold rotational symmetry of an icosahedron.
Related polyhedra
This compound shares its vertex a ...
, compound of twenty triangular prisms.
Honeycombs
There are 9 uniform honeycombs that include triangular prism cells: : Gyroelongated alternated cubic honeycomb,elongated alternated cubic honeycomb
The tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb, alternated cubic honeycomb is a quasiregular space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb (geometry), honeycomb) in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed of alternating regular octahedron, octahedra and tetrahedron, ...
, gyrated triangular prismatic honeycomb
The triangular prismatic honeycomb or triangular prismatic cellulation is a space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed entirely of triangular prisms.
It is constructed from a triangular tiling extruded into pri ...
, snub square prismatic honeycomb, triangular prismatic honeycomb
The triangular prismatic honeycomb or triangular prismatic cellulation is a space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb (geometry), honeycomb) in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed entirely of triangular prisms.
It is constructed from a triangular ti ...
, triangular-hexagonal prismatic honeycomb
The triangular prismatic honeycomb or triangular prismatic cellulation is a space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed entirely of triangular prisms.
It is constructed from a triangular tiling extruded into p ...
, truncated hexagonal prismatic honeycomb
The triangular prismatic honeycomb or triangular prismatic cellulation is a space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed entirely of triangular prisms.
It is constructed from a triangular tiling extruded into pri ...
, rhombitriangular-hexagonal prismatic honeycomb
The triangular prismatic honeycomb or triangular prismatic cellulation is a space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed entirely of triangular prisms.
It is constructed from a triangular tiling extruded into pri ...
, snub triangular-hexagonal prismatic honeycomb
The triangular prismatic honeycomb or triangular prismatic cellulation is a space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) in Euclidean 3-space. It is composed entirely of triangular prisms.
It is constructed from a triangular tiling extruded into pri ...
, elongated triangular prismatic honeycomb
Related polytopes
The triangular prism is first in a dimensional series ofsemiregular polytope
In geometry, by Thorold Gosset's definition a semiregular polytope is usually taken to be a polytope that is vertex-transitive and has all its facets being regular polytopes. E.L. Elte compiled a longer list in 1912 as ''The Semiregular Polyt ...
s. Each progressive uniform polytope
In geometry, a uniform polytope of dimension three or higher is a vertex-transitive polytope bounded by uniform facets. The uniform polytopes in two dimensions are the regular polygons (the definition is different in 2 dimensions to exclude vert ...
is constructed vertex figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.
Definitions
Take some corner or Vertex (geometry), vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connect ...
of the previous polytope. Thorold Gosset
John Herbert de Paz Thorold Gosset (16 October 1869 – December 1962) was an English lawyer and an amateur mathematician. In mathematics, he is noted for discovering and classifying the semiregular polytopes in dimensions four and higher, and ...
identified this series in 1900 as containing all regular polytope
In mathematics, a regular polytope is a polytope whose symmetry group acts transitively on its flags, thus giving it the highest degree of symmetry. All its elements or -faces (for all , where is the dimension of the polytope) — cells, ...
facets, containing all simplex
In geometry, a simplex (plural: simplexes or simplices) is a generalization of the notion of a triangle or tetrahedron to arbitrary dimensions. The simplex is so-named because it represents the simplest possible polytope in any given dimension. ...
es and orthoplex
In geometry, a cross-polytope, hyperoctahedron, orthoplex, or cocube is a regular, convex polytope that exists in ''n''- dimensional Euclidean space. A 2-dimensional cross-polytope is a square, a 3-dimensional cross-polytope is a regular octahed ...
es (equilateral triangle
In geometry, an equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides have the same length. In the familiar Euclidean geometry, an equilateral triangle is also equiangular; that is, all three internal angles are also congruent to each othe ...
s and square
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90-degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length adj ...
s in the case of the triangular prism). In Coxeter
Harold Scott MacDonald "Donald" Coxeter, (9 February 1907 – 31 March 2003) was a British and later also Canadian geometer. He is regarded as one of the greatest geometers of the 20th century.
Biography
Coxeter was born in Kensington to ...
's notation the triangular prism is given the symbol −121.
Four dimensional space
The triangular prism exists as cells of a number of four-dimensionaluniform 4-polytope
In geometry, a uniform 4-polytope (or uniform polychoron) is a 4-dimensional polytope which is vertex-transitive and whose cells are uniform polyhedra, and faces are regular polygons.
There are 47 non-prismatic convex uniform 4-polytopes. There ...
s, including:
See also
*Wedge (geometry)
In solid geometry, a wedge is a polyhedron defined by two triangles and three trapezoid faces. A wedge has five faces, nine edges, and six vertices.
A wedge is a subclass of the prismatoids with the base and opposite ridge in two parallel plane ...
References
* {{mathworld , urlname = TriangularPrism , title = Triangular prismInteractive Polyhedron: Triangular Prism
Surface area and volume of a triangular prism
Prismatoid polyhedra Space-filling polyhedra